Amazon this morning announced plans to acquire iRobot for an all-cash deal valued at $1.7 billion. The home robotics firm, best known for pioneering the robotic vacuum, was founded in 1990 by MIT Artificial Intelligence Lab members Colin Angle, Rodney Brooks and Helen Greiner. Twelve years after its founding, the company introduced the Roomba, a brand that has since become synonymous with the category, selling more than 30 million units as of 2020.
Brooks and Greiner have gone on to found and lead several other companies, while Angle has remained on-board as CEO — a position he will maintain post-acquisition.
“Since we started iRobot, our team has been on a mission to create innovative, practical products that make customers’ lives easier, leading to inventions like the Roomba and iRobot OS,” CEO Colin Angle said in a release. “Amazon shares our passion for building thoughtful innovations that empower people to do more at home, and I cannot think of a better place for our team to continue our mission. I’m hugely excited to be a part of Amazon and to see what we can build together for customers in the years ahead.”
Amazon, too, has been aggressively tackling the robotics space in the decade since it acquired Kiva Systems, though the Amazon Robotics division is focused solely on its warehouse/fulfillment play. More recently, the company has made small steps into the home with the launch of Astro, a cheery ‘bot that lacks the Roomba’s single focus.
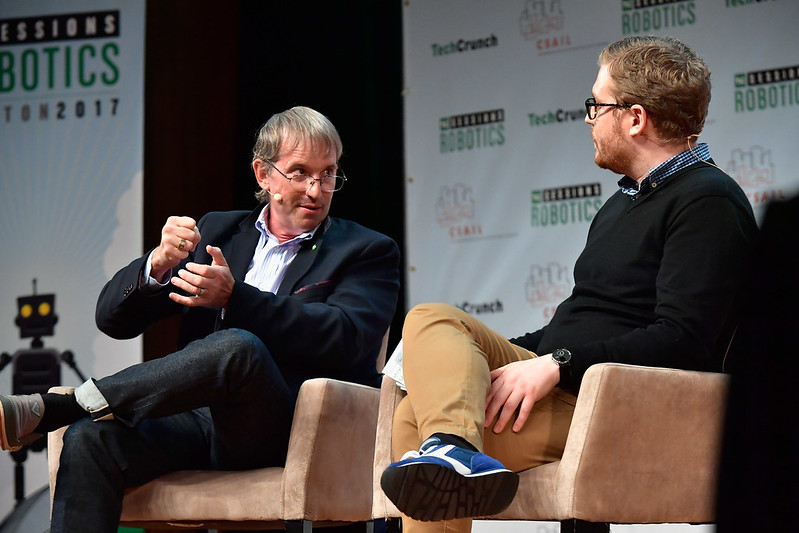

iRobot CEO Colin Angle. Image Credits: (Photo by Paul Marotta/Getty Images for TechCrunch)
“We know that saving time matters, and chores take precious time that can be better spent doing something that customers love,” Amazon Devices SVP Dave Limp said in the release. “Over many years, the iRobot team has proven its ability to reinvent how people clean with products that are incredibly practical and inventive—from cleaning when and where customers want while avoiding common obstacles in the home, to automatically emptying the collection bin. Customers love iRobot products—and I’m excited to work with the iRobot team to invent in ways that make customers’ lives easier and more enjoyable.”
Amazon and iRobot have had an increasingly close partnership over the past several years, through Roomba’s embrace of Alexa functionality and use of AWS servers. Angle, too, has often spoken about Roomba — and home robots generally — as a kind of connective tissue for the smart home. “The home of the future is a robot,” he noted in an interview with TechCrunch. “And the vacuum cleaners and the other devices are hands and eyes and appendages of the home robot. Ultimately, this smart home of the future isn’t controlled by you cell phone. If you have 200 devices, you’re not going to turn them on by pulling out your cell phone. We need a home that programs itself, and you just live in your home, and the home does the right thing based on understanding what’s going on.”
The company has, however, found difficulty recapturing the Roomba’s success — but not for lack of trying. It has experimented with several different home robot services, from cleaning gutters and pools to mopping floors and mowing the lawn. The latter arrived in the form of Terra, which has been put on indefinite hold during the pandemic. That news came in April 2020, alongside word the company had laid off 70 employees, comprising around 5% of its global workforce.
Amazon’s home robot, Astro. Image Credits: Amazon
During a Twitter Spaces last month Angle told me with regards to finally launching Terra, “What we said in the latest call is that we are working on non-floor-cleaning robots. Interpret that as you will.” Having the tremendous resources of Amazon behind it will no doubt accelerate its ability to launch non-Roomba systems. The company was founded on such experimentation, as well, having built everything from baby dolls to military machines before hitting gold with Roomba.
The company spun off its military contract wing in 2016 as Endeavor, which went on to be acquired by FLIR systems in early 2019. A year prior, iRobot spun out the telepresence robotics startup, Ava. And iRobot has made its own acquisitions, as well, purchasing connected air purifying company Aeris late last year, in a bid to diversify its in-home presences.
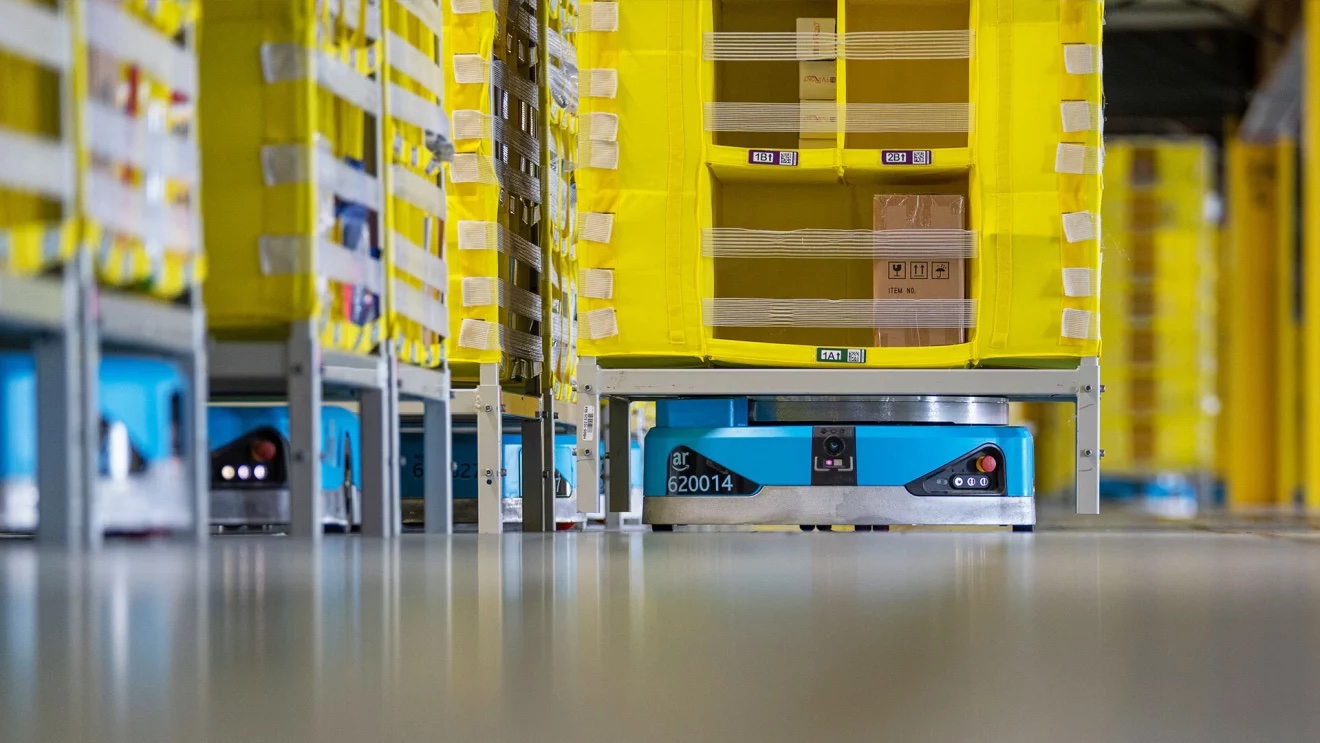

Image Credits: Amazon
The acquisition is pending the standard regulatory scrutiny. The companies will have to convince regulators — among other things — that they are maintaining the proper privacy safeguards. Amazon’s acquisition of Ring has raised all manner of red flags for advocacy groups, and its ownership of the world’s most popular in-home robot will almost certainly raise eyebrows. Recent versions of the Roomba have increasingly sophisticated sensors built-in for building 3D maps of users’ homes.
The deal ranks among Amazon’s largest during what’s been an especially active moment for the retail behemoth. It follows recent massive deals for OneMedical and MGM. If it closes, the acquisition could represent a watershed moment for home robotics. For a decade, Roomba (and the army of robot vacuums that have followed) has been the only truly mainstream home robot, as names like Anki, Jibo and Kuri have failed to reach mainstream consumers. With its acquisition of iRobot, Amazon is no doubt hoping it can do for the home what it’s succeeded in accomplishing with industrial robotics.
A decade after its acquisition of Kiva, Amazon Robotics is almost universally recognized as the warehouse and fulfillment robotics space amid a pandemic-fueled boom. Can its purchase of iRobot do the same for the home?
