Think Jack Dorsey’s jobs are tough? Well, Tom Chavez is running six startups. He thinks building businesses can be boiled down to science, so today he’s unveiling his laboratory for founding, funding and operating companies. He and his team have already proven they can do it themselves after selling their startups Rapt to Microsoft and Krux to Salesforce for a combined $1.2 billion. Now they’ve raised a $65 million fund for “super{set}”, an enterprise startup studio with a half-dozen companies currently in motion.
The idea is that super{set}t either conceptualizes a company or brings in founders whose dream they can make a reality. The studio provides early funding and expertise while the startup works from their shared space in San Francisco, plus future ones in New York and Boston. The secret sauce is the “super{set} Code,” an execution playbook plus technological tools and building blocks that guide the strategy and eliminate redundant work. “Our belief is that we can make the companies 10x faster and increase capital efficiency by 5X,” says Chavez of his partnership with super{set} co-founders Vivek Vaidya, who acts as CTO, and Jae Lim who manages the fund.
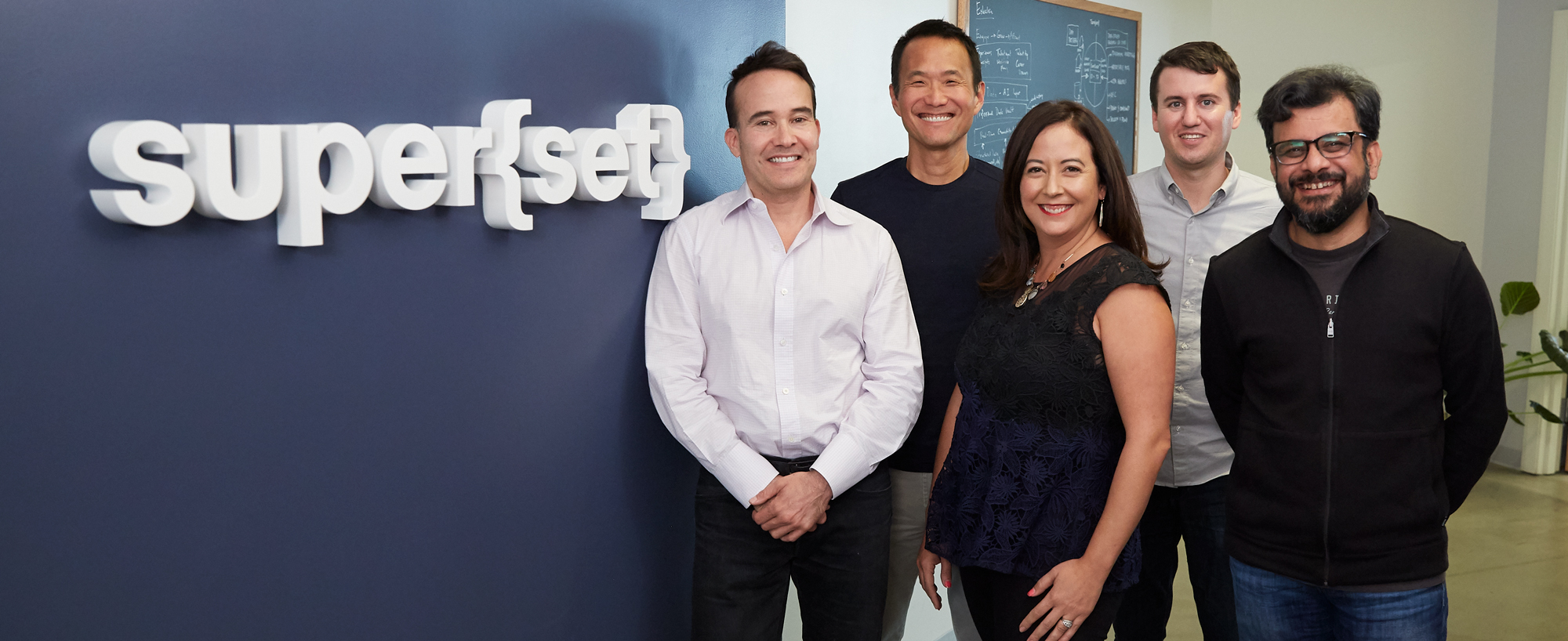

The super{set} team (from left): Tom Chavez, Jae Lim, Jen Elena, Jeremy Klein, and Vivek Vaidya
Perhaps the question isn’t whether the portfolio startups can scale, but if the humans behind them can without breaking. It’s stressful running a single company, let alone six. Even with the order of operations nailed down, each encounters unique challenges and no plan is one-size-fits-all. But after delivering 17.5X returns to their past investors, Chavez et al. have proven their power to repeatedly recognize what enterprises need and build admittedly boring but bountiful products in customer data management, and advertising yield.
The studio’s playbooks cover business plan formation, pitch strategies, go to market, revenue, machine learning, management principles, HR processes, sales methods, pipeline measurement, product sequencing, finance, legal and more. There’s also shared engineering code it provides, so each startup doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel. “I don’t think you can systemize it but I do think you can accelerate and de-risk the path,” Chavez explains.
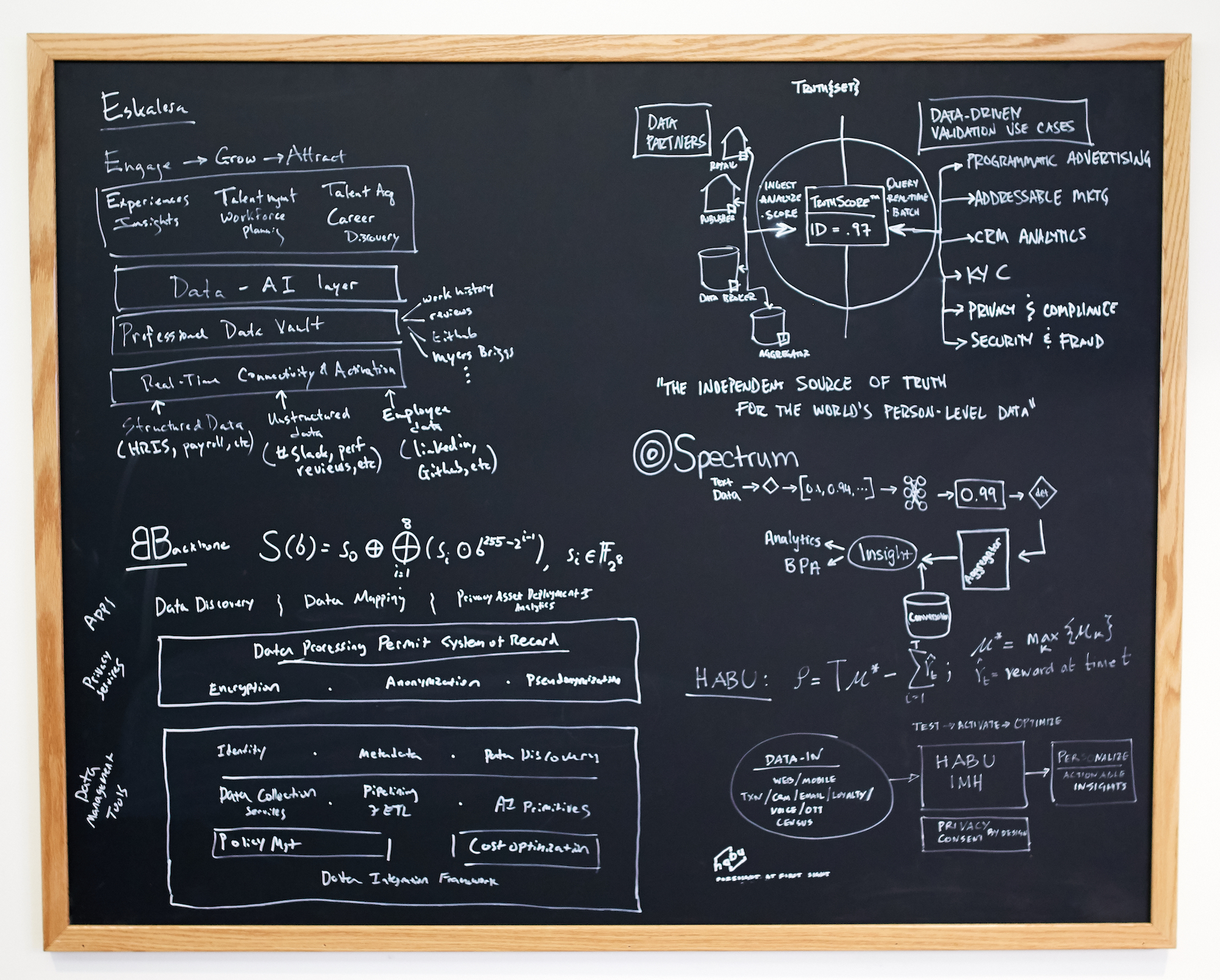
super{set} Code
Today, the first super{set} company is coming out of stealth. Eskalera helps enterprises retain top talent by tracking diversity and inclusion stats of employees to engage them with career growth and community programs. Chavez is the CEO, but plans to install a new one shortly so he can focus more time on founding more startups. There are 55 employees across the first six companies, with two already generating revenue and most ready to emerge in the next nine months.
The funding for Eskalera and other super{set} companies comes with unique terms. Because Chavez and the team aren’t just board members you hear from once a quarter but “shoulder to shoulder with the entrepreneurs” as he repeats several times in our interview, the startups pay more equity for the cash.
The hope is having seasoned leadership aboard is worth it. “We’re product people first and foremost,” Chavez tells me. “What are you going to build? Who’s going to buy it? Why? What’s the technical moat? We’re not people doing jazz hands.” The super{set} team has plenty of skin in the game, though, given Chavez himself put in a big chunk of the $65 million, and the fund sticks to a standard management fee.
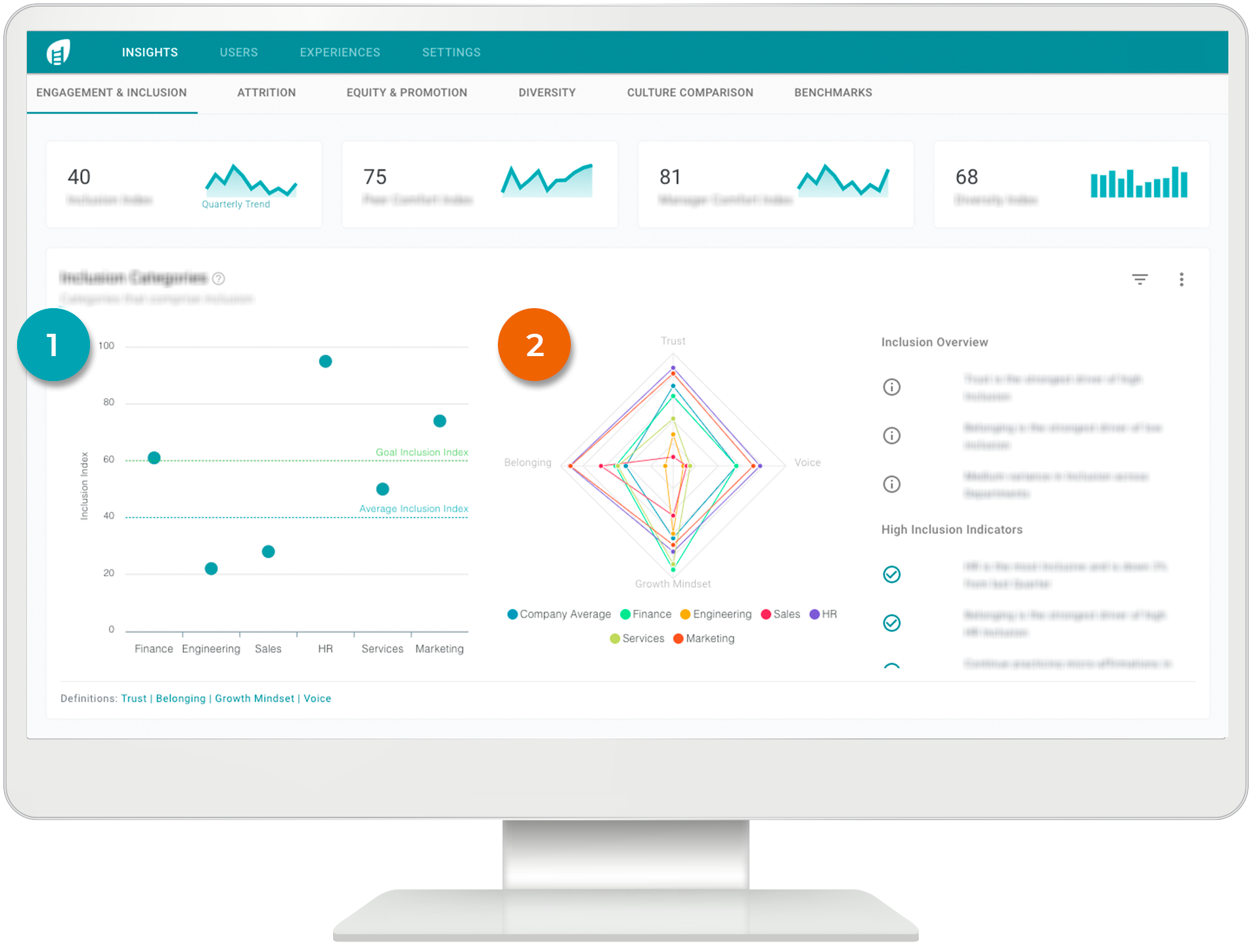
Eskalera
To supercharge the companies, super{set} brings in expert staffers in artificial intelligence, data science and more, who then align with the most relevant companies in the portfolio. They get equity grants to incentivize them to work hard on the startups’ behalf. “The worry I have about these larger funds is that they have an incentive disconnect where they work for the fees” Chavez says. His fund hopes to win through follow-on funding of its winners.

super{set} co-founder Tom Chavez
If portfolio companies hit hard times, Chavez says super{set} will stick with them. “My first company had multiple layoffs and a major pivot. We had an enterperenur that walked away. They lost conviction, but we brought that company to an $180 million exit after people said there was no effing way and that felt really good,” Chavez says of staying the course. “The good entrepreneurs have that demonic energy.” But if everyone involved agrees a project isn’t working, they’ll shutter it. “It comes back to opportunity cost of people’s time.”
Chavez has respect for studios taking different approaches, like Atomic in consumer startups, Science in e-commerce and Pioneer Square Labs, which maintains a larger fund staff. “What excites me is moving entrepreneurship a step forward. Why couldn’t we franchise this in other cities?” He hopes super{set} can attract top talent that “just want to work on cool shit” rather than getting sucked into a single company.
Can super{set} keep all the plates spinning and really lower their risk? “If we’re wrong there will be a giant orange plume streak across the sky. The early returns are promising but we have to prove it,” Chavez says. But after accruing plenty of wealth for himself, he says the thrill that keeps him in the startup game is seeing life-changing outcomes for his teams. “I have spreadsheets showing the wealth generated by employees of companies I’ve built and nothing makes me happier than seeing them pay for tuitions, property, or retiring.”
